The zebrafish is an important laboratory animal model for biomedical research and are increasingly being used for behavioral neuroscience. Tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222) is the standard agent used for euthanasia of zebrafish.
However, recent studies show that zebrafish behavior MS222 possible hostility, and clove oil may be a possible alternative. In this study, we compared the effects MS222 or clove oil as euthanasia agents in zebrafish on the volume of blood was collected and the serum levels of cortisol.
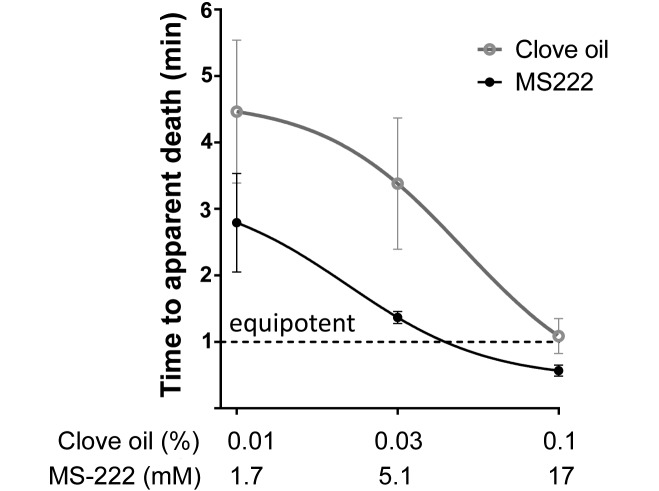
A larger amount of serum can be collected and a lower serum levels of cortisol present at euthanasia fish with clove oil as compared with equipotent doses of MS222. Euthanasia with clove oil does not blunt the expected elevation of serum cortisol levels induced by acute stress premortem.
According to our findings, clove oil is a fast-acting agent which minimizes cortisol responses to euthanasia in zebrafish and allows the collection of a large volume of blood postmortem. These results represent a significant improvement in the method of euthanasia for zebrafish.
Serum C-reactive protein and white blood cell level as markers of successful percutaneous drainage of acute sterile peripancreatic fluid collection.
BACKGROUND
Percutaneous drainage is not a method of therapy is widely used recently to evacuate sterile peripancreatic fluid collections in patients with severe acute pancreatitis.However, many clinical studies have shown positive effects.
OBJECTIVE
We tested changes in laboratory parameters of serum C-reactive protein (CRP), complement factor 3-4 (C 3-4), tumor necrosis factor a (TNF-a), amylase, lipase and white blood cell (WBC) count in patients treated with percutaneous drainage.
METHOD
10 patients with severe acute pancreatitis with peripancreatic fluid collections were monitored.Laboratory parameters and the amount of fluid drained was measured on the 1st, 5th and 10th day. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistics for Windows (Version 7.0) software. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
We found a significant positive correlation between serum levels of CRP and WBC and drained fluid volume. We use this parameter as a marker of successful percutaneous drainage in the case of patients with severe acute pancreatitis complicated with sterile peripancreatic fluid.There no significant change in levels of C 3-4, tumor necrosis factor-Î + -, amylase and lipase.
CONCLUSION
Monitoring of serum CRP and WBC levels may be recommended for follow-up after percutaneous drainage of peripancreatic fluid.
BACKGROUND
CRP: C-reactive protein TNFÎ + -: Tumor Necrosis Factor a, C3-4: Complementary 3-4 WBC: White Blood Cells CT: Computed Tomography.

